SIP Accounts
SIP accounts let you use your FlyNumber with any SIP-compatible phone or softphone app—like a desk VoIP phone, Zoiper, Groundwire, or Linphone. Instead of using the FlyNumber phone system app, you get credentials (username, password, server) to configure your preferred device.
When to Use SIP Accounts
| Use Case | SIP Account | Phone System App |
|---|---|---|
| Desk VoIP phones (Yealink, Polycom, etc.) | Yes | No |
| Prefer a specific softphone app | Yes | No |
| Want the simplest setup | No | Yes |
| Mobile push notifications | Yes (Groundwire, Zoiper, etc.) | Yes (built-in) |
| One user across multiple devices | Via SIP forking | Yes (unlimited devices) |
| Multiple SIP lines on one device | Yes | N/A |
See Routing Options for two ways to configure how calls reach your SIP account—either direct assignment or through call flows.
For simple use cases, assign a FlyNumber directly as the DID Number to set up inbound and outbound calls without needing to create call flows. For more complex scenarios, leave the DID Number empty and integrate the SIP account into your call flows using a Ring Group or Queue module.
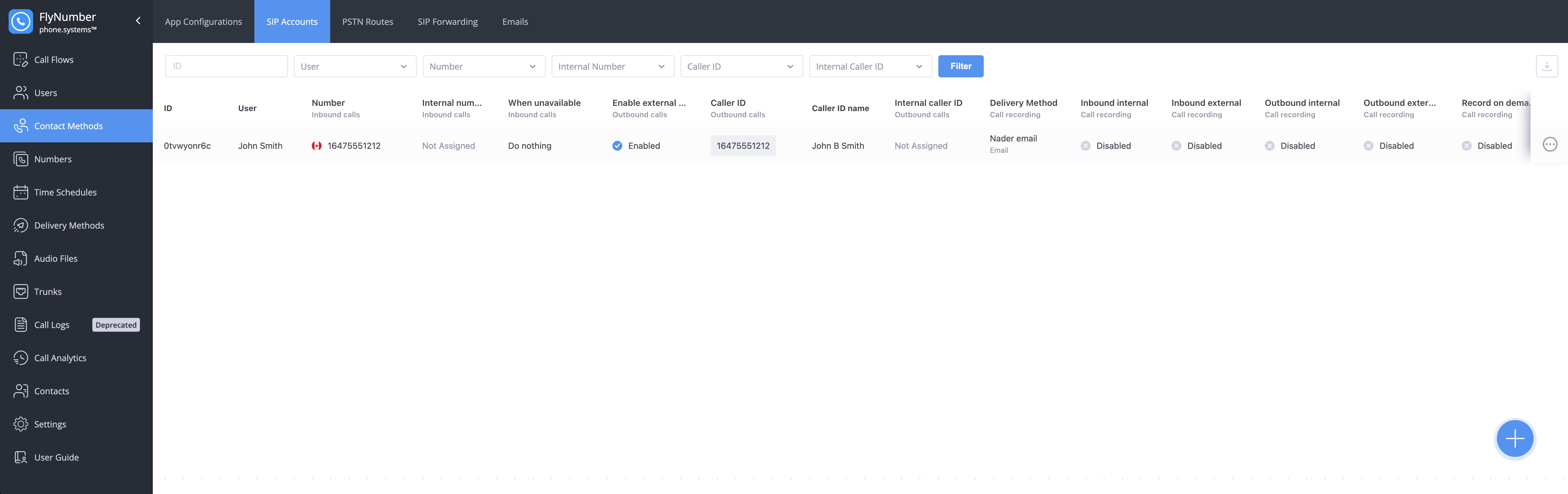
Interface Fields
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| ID | Unique identifier for the SIP account |
| User | Name of the user assigned to this account |
| Number | FlyNumber assigned for inbound calls |
| Internal number | Extension for internal calling |
| When unavailable | Action taken when user can't answer |
| Allow Call Transfer | Indicates if call transfer is enabled |
| Enable external outbound calls | Whether external calling is allowed |
| Caller ID | Number used for outbound calls |
| Caller ID name | Display name for outbound calls |
| Internal caller ID | Identity for internal calls |
| Delivery Method | Where call recordings are sent |
| Inbound internal | Call recording setting for internal incoming calls |
| Inbound external | Call recording setting for external incoming calls |
| Outbound internal | Call recording setting for internal outgoing calls |
| Outbound external | Call recording setting for external outgoing calls |
| Record on demand | Whether manual call recording is enabled |
You can drag columns left or right to rearrange them in any order you prefer. You can also download your SIP account configurations by clicking the download icon in the top right corner.
Creating a SIP Account
To create a new SIP account:
- Click the + button in the bottom right corner
- Configure the following sections:
General Settings

Select the user who will own this SIP account. The user's settings and permissions will apply to this account.
Outbound Call Settings
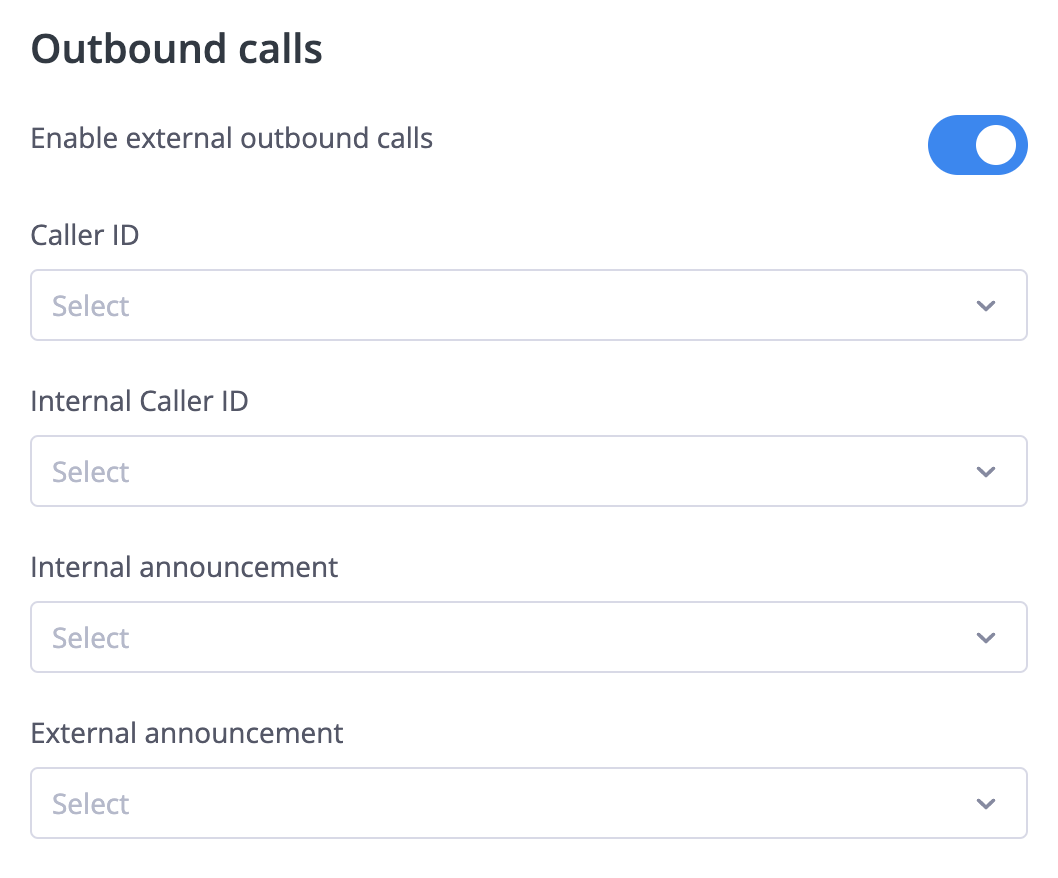
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable external outbound calls | Toggle ability to make calls to regular phone numbers |
| Caller ID | Which FlyNumber appears when you call external numbers |
| Internal Caller ID | Your identity when calling other extensions in the system |
Outbound Announcements
Announcements are audio messages that play when your outbound call is answered. They're useful for compliance, branding, or providing context to the person answering.
| Announcement Type | When It Plays | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Announcement | When an internal extension answers your call | "This call may be recorded for training purposes" |
| External Announcement | When an external number answers your call | "This is a call from [Company Name]" or a legal disclaimer |
- Recording notifications: "This call is being recorded"
- Caller identification: Helps the recipient know who's calling before they speak
- Legal compliance: Required disclosures in some industries or regions
- Branding: Professional greeting before conversation begins
Announcements play to the recipient of your outbound call, not to you. The person answering hears the announcement before the conversation begins.
When making outbound calls, use the E.164 format without any prefixes (no 011, 00, or + symbol):
- US/Canada numbers: Country code (1) + area code + number
- Example: 19176282411
- UK numbers: Country code (44) + number
- Example: 44203603115
- Other countries: Follow the same pattern with appropriate country code
Call Recording
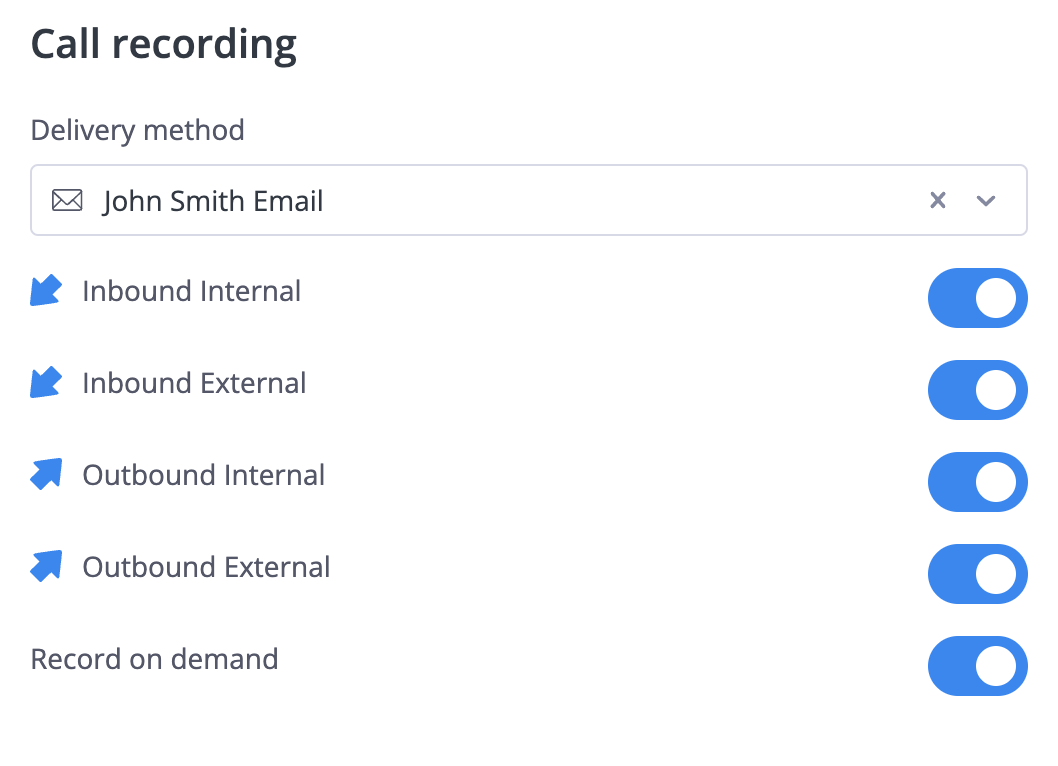
Configure which calls to record and where recordings are delivered. See Call Recording Configuration for all available options including delivery methods and cloud storage integration.
Advanced Settings
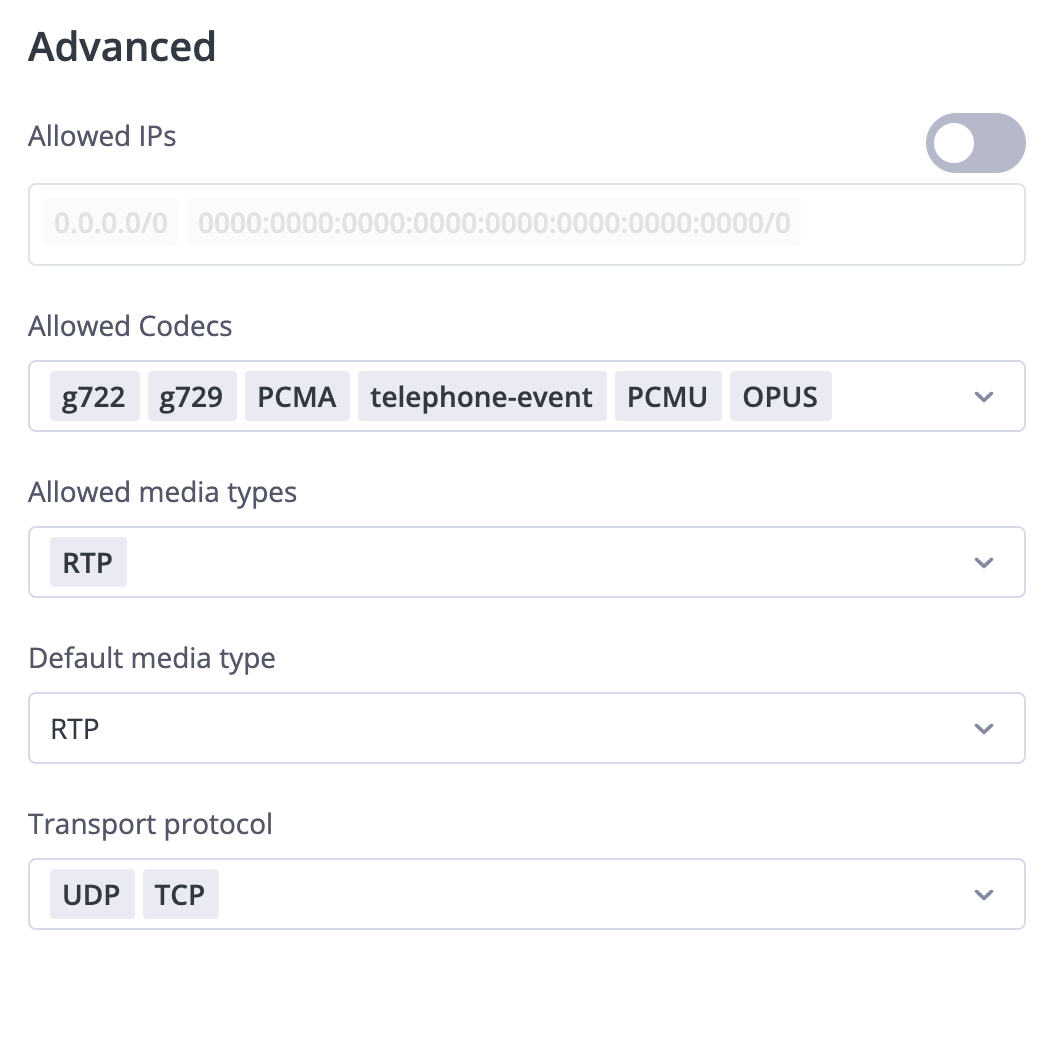
Configure technical settings:
Allowed IPs
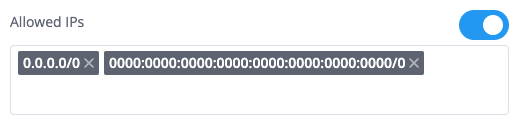
- Enable to restrict registration to specific IP addresses
- Support for both IPv4 and IPv6
- CIDR notation allowed for IP ranges
Codecs
Codecs determine how audio is compressed during calls. Different codecs offer trade-offs between audio quality and bandwidth usage.
| Codec | Quality | Bandwidth | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OPUS | Excellent | Variable (6-510 kbps) | Best overall quality, adapts to network conditions |
| G722 | HD Voice | 64 kbps | High-quality calls on good connections |
| PCMU (G.711 μ-law) | Good | 64 kbps | North America standard, widely compatible |
| PCMA (G.711 A-law) | Good | 64 kbps | International standard, widely compatible |
| G729 | Acceptable | 8 kbps | Low bandwidth situations |
| GSM | Acceptable | 13 kbps | Mobile network compatibility |
| telephone-event | N/A | Minimal | Required for DTMF tones (keypad presses) |
The telephone-event codec is required for DTMF tones to work. Without it, pressing keys during calls (for IVR menus, entering PINs, using feature codes) won't function.
For most users, keep the defaults. If you experience audio issues:
- On slow connections: Prioritize G729 or GSM
- For best quality: Prioritize OPUS or G722
- For maximum compatibility: Include PCMU and PCMA
Media Types
Media types control how audio data is transmitted between your device and the system.
| Media Type | Encryption | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| RTP | None | Standard, unencrypted audio (default) |
| SRTP-SDES | Yes | Encrypted audio using key exchange in SIP signaling |
| SRTP-DTLS | Yes | Encrypted audio using DTLS key exchange (more secure) |
For most internal or trusted network use, RTP is sufficient. Use SRTP options when calls traverse untrusted networks and security is a priority.
Transport Protocol
Transport protocols determine how SIP signaling (call setup, teardown) is transmitted.
| Protocol | Encryption | Port | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| UDP | No | 5060 | Most common, lowest latency |
| TCP | No | 5060 | Better for unreliable networks, larger messages |
| TLS | Yes | 5061 | Encrypted signaling for secure environments |
| WSS | Yes | 443 | WebSocket Secure, used by web-based clients |
- UDP: Default choice for most setups—fast and efficient
- TCP: Use if you experience packet loss or NAT issues with UDP
- TLS: Use when security policies require encrypted signaling
- WSS: Typically for browser-based softphones
You can switch between UDP and TCP directly in the phone system panel. TLS and WSS require support to enable.
Encrypted options (SRTP media types and TLS/WSS transport) are disabled by default. Contact support to enable these features for your account.
SIP Credentials
After saving, click the edit button (three dots on the right) to view the SIP credentials needed for your client:
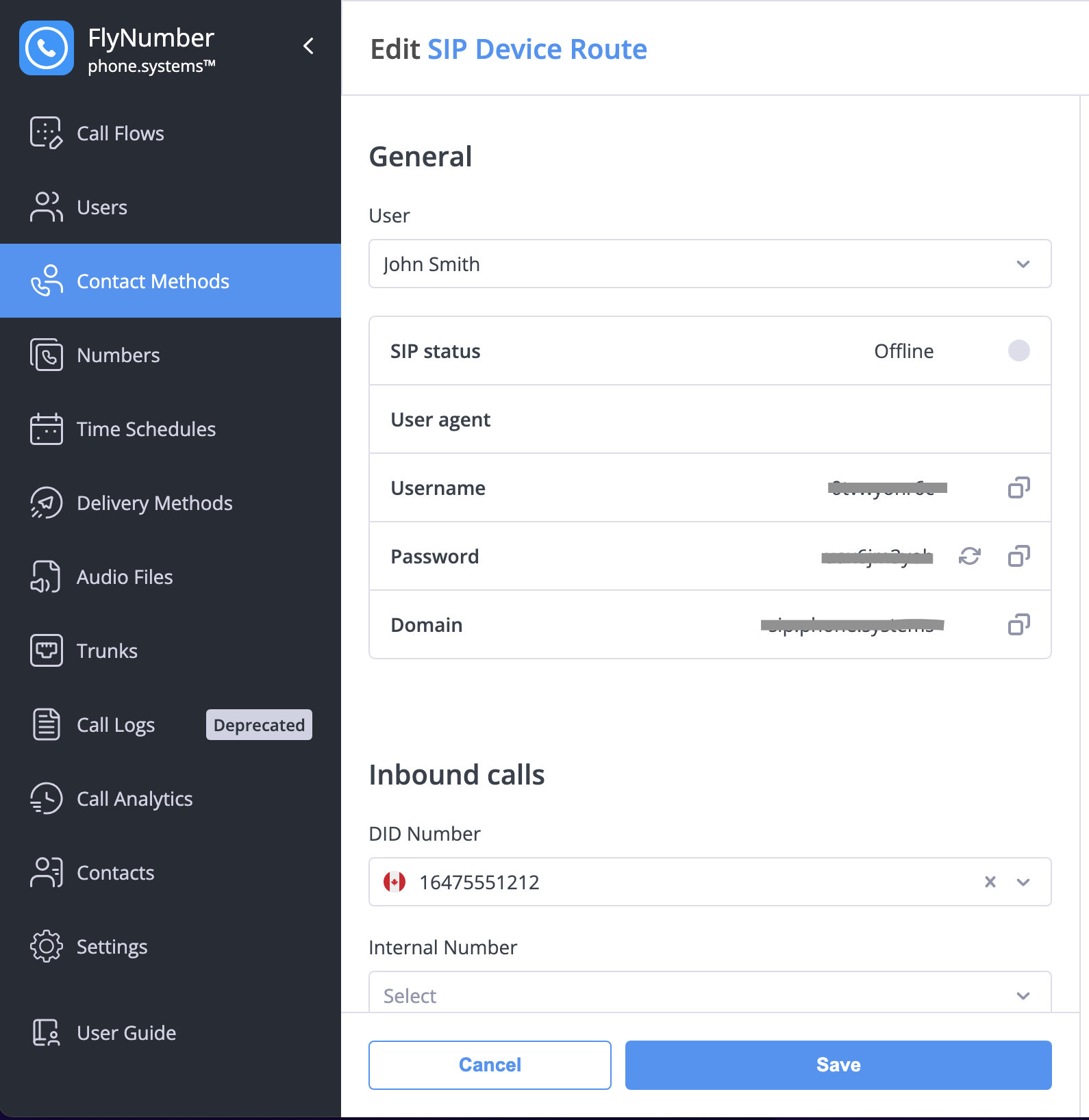
If you added this SIP account to a ring group, you can click the gear icon of the ring group module, then the edit icon on the SIP account destination to also view the SIP credentials.
Configuring Your SIP Client
Once you have your SIP credentials, configure your phone or softphone with these settings:
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Username | From SIP credentials |
| Password | From SIP credentials |
| Domain/Server | From SIP credentials |
| Transport | UDP (or as configured in Advanced Settings) |
| Port | 5060 (UDP/TCP) or 5061 (TLS) |
Popular SIP clients that work with FlyNumber:
- Zoiper (iOS, Android, Windows, Mac, Linux)
- Groundwire (iOS, Android)
- Linphone (iOS, Android, Windows, Mac, Linux)
- Bria (iOS, Android, Windows, Mac)
- MicroSIP (Windows, free)
Most desk phones from Yealink, Polycom, Grandstream, and Cisco also work.
Call Transfers
SIP accounts support call transfers when enabled. See Call Transfers for details on attended and unattended transfers.
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Likely Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Can't register | Wrong credentials | Double-check username, password, and domain |
| One-way audio | Firewall/NAT issue | Check firewall allows UDP on RTP ports (16384-32767) |
| No audio at all | Codec mismatch | Ensure your client supports at least one of the enabled codecs |
| DTMF not working | Missing codec | Make sure telephone-event is enabled |
| Intermittent drops | Network issues | Try TCP instead of UDP, or check network stability |